这篇笔记介绍lecture12,集合论的内容。
计算问题
如果某个计算问题(Computational Problem)只会严格遵循有限的指令,且在一定次数的操作后一定会终止,则它是可计算的。
基本概念与性质
集合(set)是不同对象的无序收集,这里的对象可以是任何东西,包括其它集合。如果 a 是集合 A 中的元素,则 a 属于 A ,即 a∈A ;否则,则 a 不属于 A ,即 a∈/A 。
在元素较少时,可以直接用大括号表示集合,如 {1,2,3,4} 。许多常见集合用大写字母表示,如 C 为复数集, U 为考虑范围内所有元素的集合。集合还可以用内涵表示法表示,写为 {x∣P(x)} 或 {x:P(x)} 。这里的 P(x) 是一个谓词逻辑公式,这个集合表示使 P(x) 为真的所有 x 的集合,如 {x∣x is a prime number}={2,3,5,7,...} 。
如果集合 A 与 B 中的元素是完全相同的,则 A 与 B 相等,即 A=B⇔(∀x)(x∈A↔x∈B) 。如果集合 A 中的每个元素都出现在集合 B 中,则 A 包含于 B ,也称 A 是 B 的子集(subset),即 A⊆B⇔(∀x)(x∈A→x∈B) 。如果 A 是 B 的子集且 A=B ,则 A 是 B 的真子集(proper subset),即 A⊂B⇔(A⊆B∧A=B) 。空集是任何集合的子集。
集合有三条性质:无序性(unorder)、相异性(distinction)、确定性(deterministic)。无序性指,集合中元素的排列顺序不重要。相异性指,集合中不能出现两个(或多个)同样的元素。确定性指,对于元素 a ,只存在 a∈A 或 a∈/A 两种情况,并且 a 是否属于 A 是确定的且互斥的。
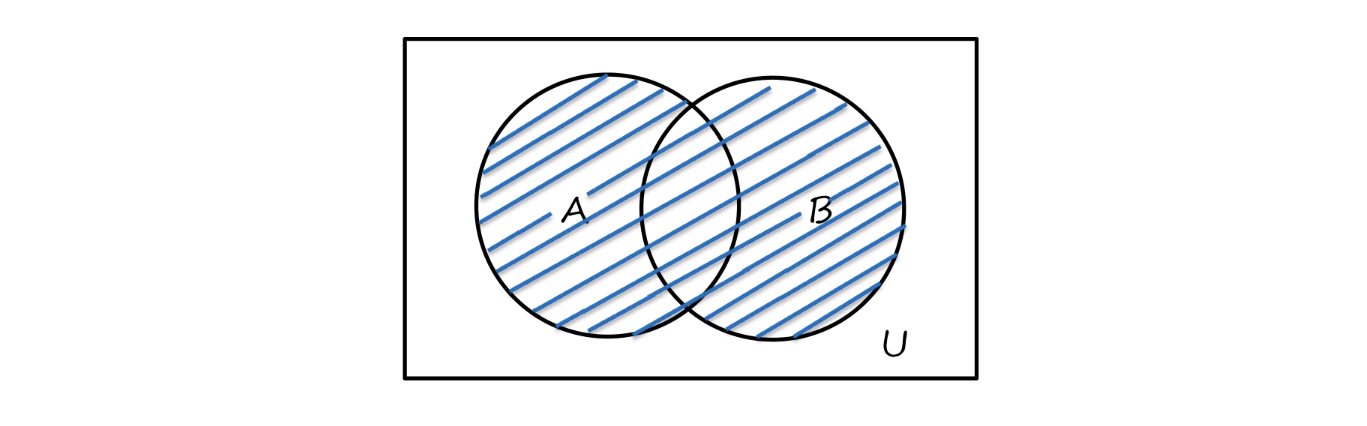
- 并(union)
A∪B={x∣x∈A∨x∈B}
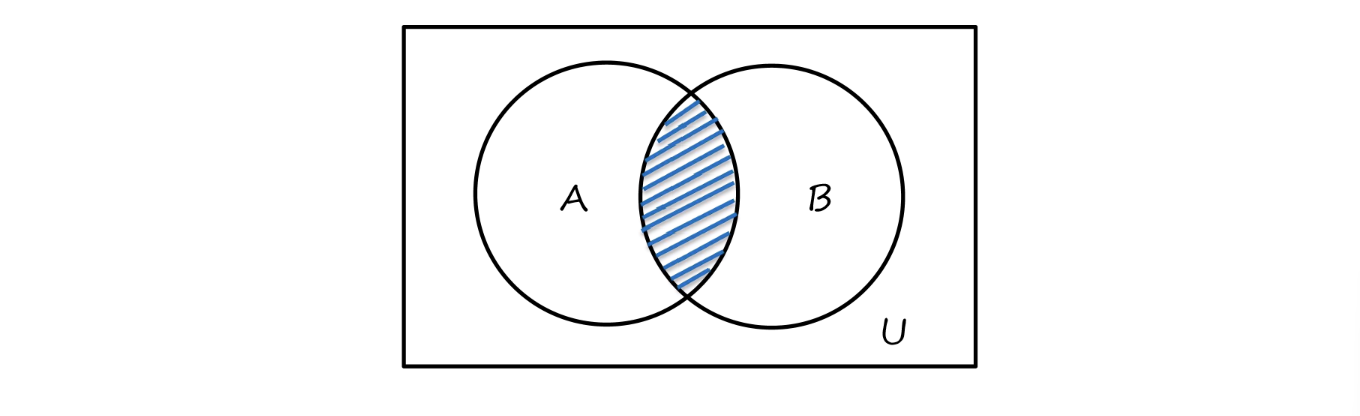
- 交(intersection)
A∩B={x∣x∈A∧x∈B}
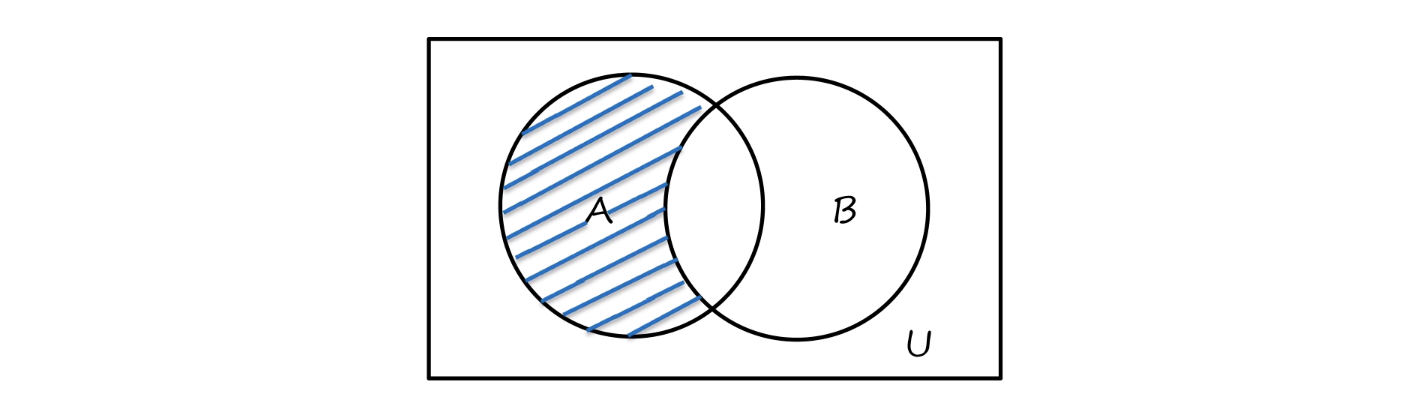
- 差(difference)
A−B={x∣x∈A∧x∈/B}
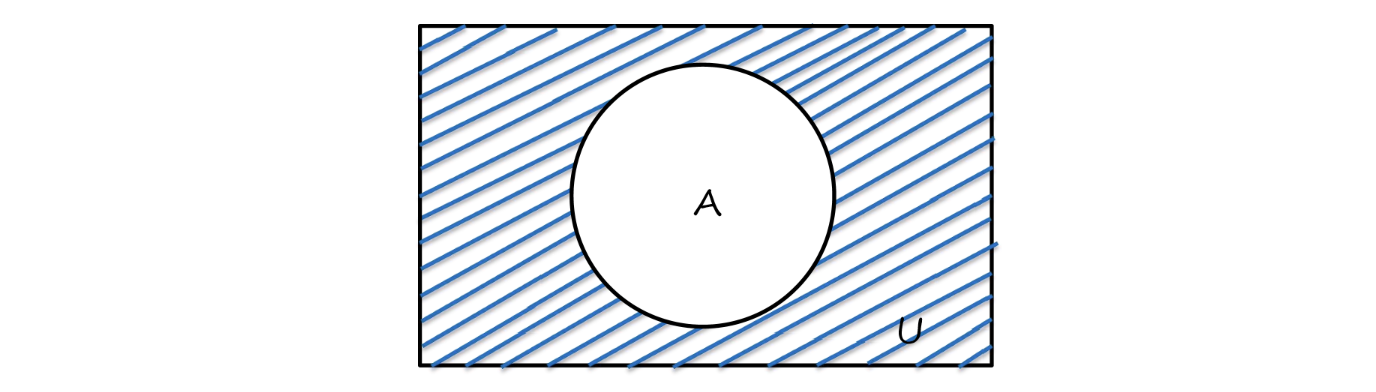
- 补(complement)
−A or A={x∣x∈U∧x∈/A}
- 对称差(symmetric difference)
A⊕B={x∣x∈A∨x∈B}=(A−B)∪(B−A)
(这里的 ∨ 表示异或)
-
广义并(generalized union)
∪A={x∣(∃z)(z∈A∧x∈z)}
∪∅=∅
-
广义交(generalized intersection)
∩A={x∣(∀z)(z∈A→x∈z)}
∩∅ 未定义。
注意广义并和广义交运算要求集合的元素也是集合。
同一律(identity law)
- A∩U=A
- A∪∅=A
交换律(commutative law)
- A∪B=B∪A
- A∩B=B∩A
零律(domination law)
- A∪U=U
- A∩∅=∅
结合律(associative law)
- A∪(B∪C)=(A∪B)∪C
- A∩(B∩C)=(A∩B)∩C
幂等律(idempotent law)
- A∪A=A
- A∩A=A
分配律(distributive law)
- A∪(B∩C)=(A∪B)∩(A∪C)
- A∩(B∪C)=(A∩B)∪(A∩C)
双补律(complementation law)
- (A)=A
补余律(complement law)
- A∪A=U
- A∩A=∅
吸收率(absorption law)
- A∪(A∩B)=A
- A∩(A∪B)=A
摩根律(De Morgan's law)
- A∩B=A∪B
- A∪B=A∩B
- A−(B∩C)=(A−B)∪(A−C)
- A−(B∪C)=(A−B)∩(A−C)
相关问题证明
集合论的相关基础证明有三种解题方案:使用定义、转换为逻辑等式、使用相关定律。可以用韦恩图辅助理解,但不能将其用于证明。
下面是三个使用了不同证明方法的例子。
- proof A∪B=B⇒A⊆B
For any x, assume x∈A∴x∈A∪B∵A∪B=B ∴x∈B∴A⊆B
- proof A−(B∪C)=(A−B)∩(A−C)
x∈A−(B∪C)⇔(x∈A)∧(x∈/(B∪C))⇔x∈A∧x∈/B∧x∈/C⇔(x∈A∧x∈/B)∧(x∈A∧x∈/C)⇔(x∈(A−B))∧(x∈(A−C))⇔x∈((A−B)∩(A−C))
- proof A∪(B∩C)=(C∪B)∩A
A∪(B∩C)=A∩B∩C=A∩(B∪C)=(B∪C)∩A=(C∪B)∩A
语言识别问题
在计算问题中,判定问题可以通过decider解决,但其它问题不行。要解决其它问题,可以找出可能的答案,用decider验证答案��是否正确。
某些这个过程(在某种意义上)可以转化为membership problem。定义量词 P ,使得使 P(x) 为真的 x 是有效输入且符合问题的要求。令 S={x∣P(x)} ,判断 x 是否为有效答案时,只需要判断 x 是否在 S 中。
用语言识别问题(a membership problem of language)来描述,原问题可以改为“Give a language L and take w as input, determine whether w∈L”。




